10 KiB
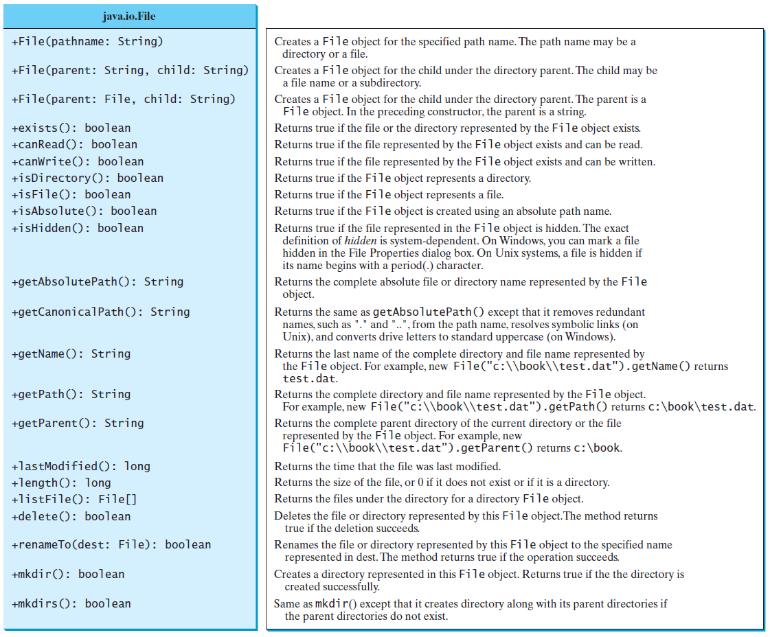
The File class is intended to provide an abstraction that deals with most of the machine-dependent complexities of files and path names in a machine-independent fashion. The filename is a string. The File class is a wrapper class for the file name and its directory path.
文件类提供了一个与机器(操作系统)无关的文件和路径操作的封装;文件类主要用作文件名和路径的操作,并不对文件本生的内容进行操作。
注意:
- 在文件系统中有路径的概念,路径的分隔符是“/”叫做斜杠;Windows系统中的文件分割符与其他的操作系统是相反的“\”反斜杠,这可能会造成一些困扰,最典型的就是字符串转义。在所有的语言中,反斜杠(\)被用作字符串的转义字符,例如“\n”代表换行,“\t”代表tab等。在Java编程当中,凡是遇到路径分割符的地方,只需要使用斜杠“/”就可以了,Java会根据运行的操作系统自动进行转换和处理。例如:“C:/windows/cfg.ini”,最好不要使用反斜杠,如果需要反斜扛,需要这样写:“C:\\windows\\cfg.ini”,因为反斜杠在字符串中代表转义。
- 你们会发现,在URL,例如“http://www.baidu.com/qurey/index.html”,这样的字符串中,斜杠也是路径分隔符,因此斜杠在大多数情况下都是通用的,尽量不要用反斜杠代表路径分割。
- Windows文件系统具有盘符的概念,在其他大多文件系统中是没有这个概念的。例如Linux中,一个逻辑盘可以被分配到一个目录当中,linux的文件系统是从"/"开始的,叫做根-root。
- Windows文件系统中,文件名是不区分大小写的;在其他多数文件系统中文件名是区分大小写的(case sensitive),这一点需要特别注意。
1. 文件类
文件类是一个对文件名和路径操作的类。可以进行如下操作:
- 文件是否存在;
- 是否可读;
- 是否可写;
- 是否是目录(目录是特殊的文件);
- 是否是文件;
- 是否是绝对路径;
- 是否隐藏文件;
- 得到文件的绝对路径;
- 文件修改和范围时间;
- 文件重命名;
- 新建目录;
- 目录列表
- ...
1.1. 读取文件属性
注意第一行的包引入。
import java.io.File;
public class TestFileClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("src/TestFileClass.java");
System.out.println("Does it exist? " + file.exists());
System.out.println("The file has " + file.length() + " bytes");
System.out.println("Can it be read? " + file.canRead());
System.out.println("Can it be written? " + file.canWrite());
System.out.println("Is it a directory? " + file.isDirectory());
System.out.println("Is it a file? " + file.isFile());
System.out.println("Is it absolute? " + file.isAbsolute());
System.out.println("Is it hidden? " + file.isHidden());
System.out.println("Absolute path is " + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("Last modified on " + new java.util.Date(file.lastModified()));
}
}
构造参数传的字符串代表一个文件,注意这里使用的是相对路径(也可以是绝对路径)。其实也可以是一个文件夹的路径,在操作系统中,文件夹是一种特殊的文件。我们可以看到,file这个对象其实是一个文件,可以对文件的属性进行读取。
这里不对File类的所有功能进行分析,以后很多情况下,需要用一个File对象作为参数。大多时候,这个File对象代表对应的文件。
2. 文本文件操作
A File object encapsulates the properties of a file or a path, but does not contain the methods for reading/writing data from/to a file. In order to perform I/O, you need to create objects using appropriate Java I/O classes. The objects contain the methods for reading/writing data from/to a file. This section introduces how to read/write strings and numeric values from/to a text file using the Scanner and PrintWriter classes.
File 对象封装了对文件名和路径的操作,但是不对文件的具体内容进行读写。为了完成I/O(文件输入输出)操作,需要使用适当的I/O操作类。这些I/O操作类具有读写文件的能力。这一节,我们介绍使用Scanner和PrintWriter类对文本文件中的字符串进行操作。
2.1. PrintWrite类
可以看到,PrintWrite如同一个打印机,向文件打印不同类型的数据(这些数据被转换成字符串的方式,而不是二进制的方式)。该类也有println和printf函数,和前面讲的控制台输出函数是一样的,只不过不是控制台输出,而是输出到文件。注意操作系统不一样,回车换行字符不一样;Windows是\r\n,linux是\n。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class WriteData {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new java.io.File("D:/scores.txt");
if (file.exists()) {
System.out.println("File already exists");
System.exit(1);
}
// Create a file
PrintWriter output = new PrintWriter(file);
// Write formatted output to the file
output.print("John T Smith ");
output.println(90);
output.print("Eric K Jones ");
output.println(85);
// Close the file
output.close();
}
}
- 首先建立了一个File对象,其文件名是
D:/scores.txt;判断文件是否存在,如果存在,退出出返回1。 - 如果不存在,建立一个PrintWriter的对象ouput,其构造函数的参数正式前面的File对象,代表向哪个文件进行操作。PrintWriter的构造函数有多个,可以接受一个字符串代表文件名,也可以接受一个File对象代表文件。
- 后面就是日常的操作了,看看结果。
- 别忘了,文件操作完成后,需要关闭PrintWriter。
John T Smith 90
Eric K Jones 85
注意:File对象没有close()方法,因为File对象不对文件的具体内容进行操作。
主函数是有返回值的,返回一个整数;对于多数操作系统来说,返回值代表程序是否运行成功;一般返回值是0代表成功,没有错误;非零代表有错误。
2.2. 不要别忘记关闭文件
和C一样,文件用完后需要关闭。因为文件属于共享I/O资源,可能有多个程序对同一文件进行操作,如果忘记关闭将出现很多意想不到的问题。Java提供了一个语法结构来保证文件总是被正确关闭。
public class WriteDataWithAutoClose {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
java.io.File file = new java.io.File("scores.txt");
if (file.exists()) {
System.out.println("File already exists");
System.exit(0);
}
try (
// Create a file
java.io.PrintWriter output = new java.io.PrintWriter(file);
) {
// Write formatted output to the file
output.print("John T Smith ");
output.println(90);
output.print("Eric K Jones ");
output.println(85);
}
}
}
注意上面的的语法结构,try后面是一个括号,这个括号中可以有多条语句(上述只有一条);而且这个用小括号包裹的语法块不是所有的语句都可以写的,只能是构造对象的语法,而且对象必须实现了Closeable这个接口。
public class PrintWriter extends Writer {...}
public abstract class Writer implements Appendable, Closeable, Flushable {...}
PrinterWriter 从抽象类Writer扩展;Writer这个类实现了Closeable这个接口。
因此:try语法块中小括号包含的语句必须是实现了Closeable接口的对象构造语句。
后面大括号内包含的语法块就好理解了,就是说这里的语句再执行完成后,不需要关闭小括号中语句打开的资源,Java会自动关闭。
2.3. Scanner可以读取文件
还记得以前学过的Scanner对象,从控制台读取数据吗?
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
构造函数的参数是System.in表示从标准输入读取(看具体定义,一般是控制台);如果把这个参数换成是File对象,就可以从文本文件读取了。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReadData {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Create a File instance
java.io.File file = new java.io.File("d:/scores.txt");
// Create a Scanner for the file
Scanner input = new Scanner(file);
// Read data from a file
while (input.hasNext()) {
String firstName = input.next();
String mi = input.next();
String lastName = input.next();
int score = input.nextInt();
System.out.println(firstName + " " + mi + " " + lastName + " " + score);
}
// Close the file
input.close();
}
}
注意:这时就需要使用close()来关闭Scanner对象了,因为这里的input是对文件I/O进行操作。
你可以尝试使用try(...){...}的语法结构来自动关闭Scanner对象,因为Scanner也是实现了Closeable的接口。
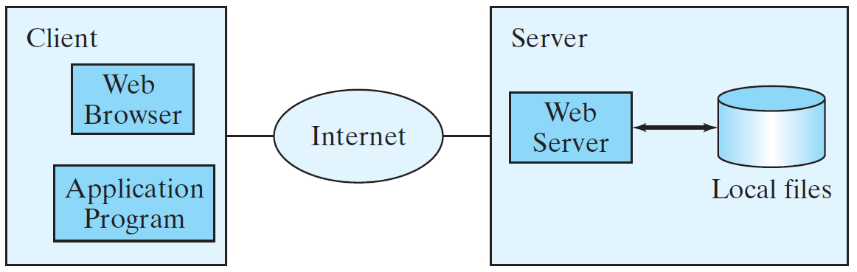
2.4. 从url读取数据
WEB上的文件(HTML)也是文件,因此也可以读取,不过需要连接到互联网。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReadFileFromURL {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("Enter a URL: ");
String URLString = new Scanner(System.in).next(); // 从控制台读取URL
try {
java.net.URL url = new java.net.URL(URLString); // 建立一个URL对象,输入参数是刚刚读取的URL字符串
int count = 0;
Scanner input = new Scanner(url.openStream()); // 这里是流编程,url.openStream 返回一个InputStream对象
while (input.hasNext()) { // 这里就一样了
String line = input.nextLine();
count += line.length();
System.out.println(line);
}
System.out.println("The file size is " + count + " bytes");
} catch (java.net.MalformedURLException ex) {
System.out.println("Invalid URL");
} catch (java.io.IOException ex) {
System.out.println("IO Errors");
}
}
}
3. 重点
- 掌握File类的基本使用;
- 掌握PrintWriter的基本使用;
- 掌握Scnner读取文本文件内容的基本使用;
- 了解 try(...){...}语法;